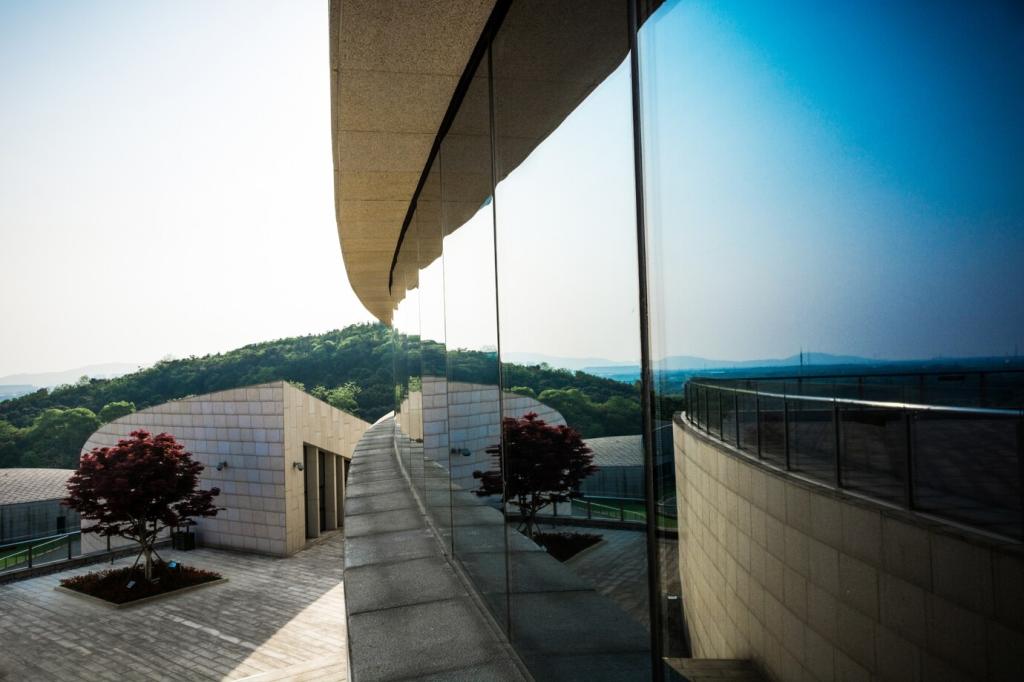
Green Architecture for Modern Living
Green architecture, also known as sustainable or eco-friendly architecture, represents the future of modern living by integrating environmentally mindful practices into the design, construction, and operation of buildings. This approach not only emphasizes the use of renewable materials and energy-efficient solutions but also seeks to create harmonious spaces that promote healthy lifestyles and minimize the ecological footprint. In an era defined by climate change and resource constraints, green architecture stands at the intersection of innovative technology and responsible stewardship, shaping spaces that respond to both human needs and environmental imperatives.

Sustainable Building Materials
Recycled and upcycled resources are at the forefront of sustainable construction. Materials such as reclaimed wood, recycled steel, and repurposed stone provide architects and builders with high-quality options that save energy and minimize landfill contributions. Utilizing these resources often requires creative design solutions, as architects adapt materials originally meant for other purposes or structures into new and innovative applications. Beyond reducing waste, using recycled content can lend unique character and history to a building, connecting occupants to stories from the past while serving the needs of the present.
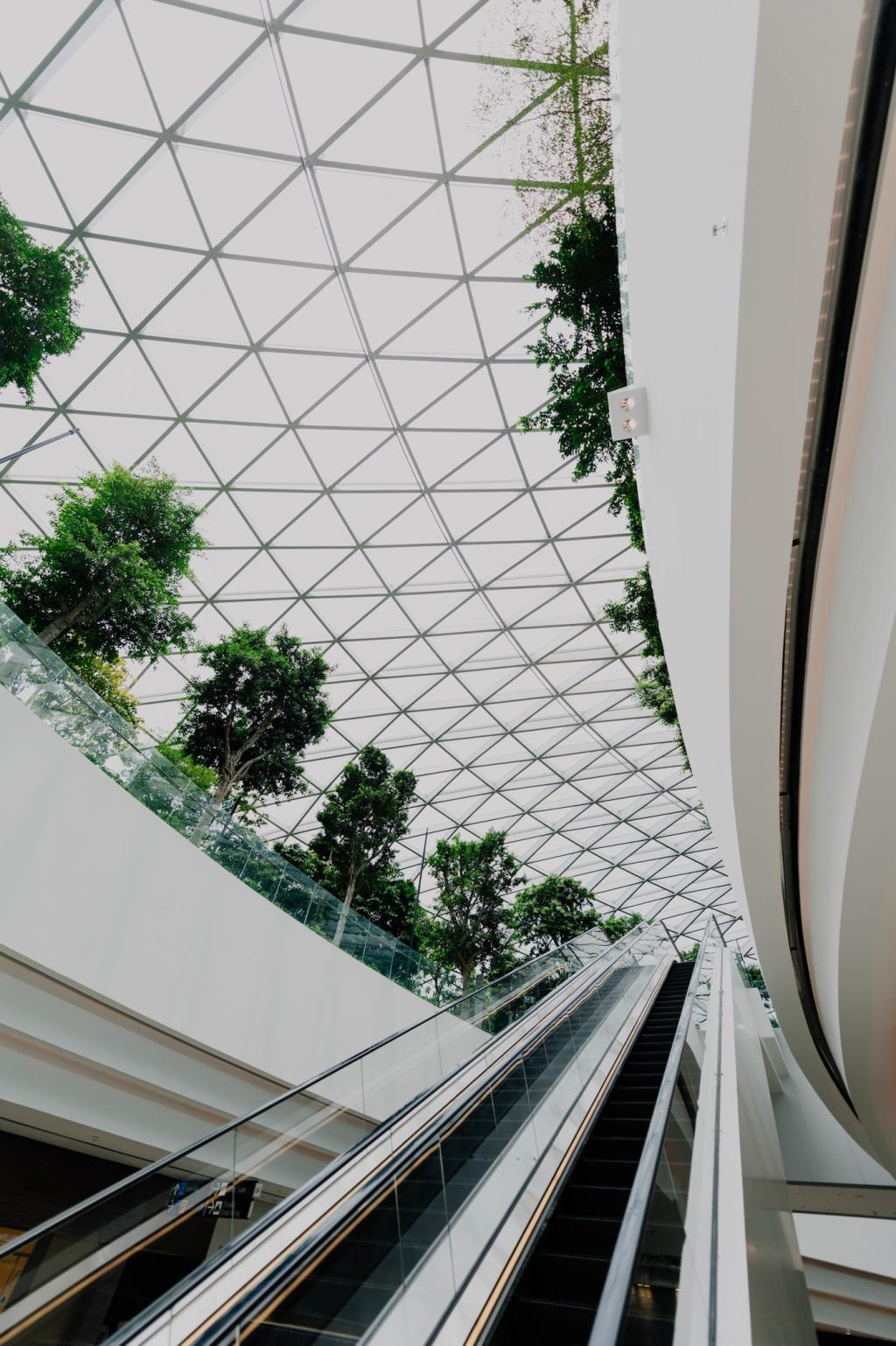

Passive Design Strategies
Passive design harnesses the natural environment to regulate a building’s temperature, light, and ventilation. Techniques like orientation, shading, natural ventilation, and thermal mass reduce dependence on artificial heating and cooling systems. By meticulously analyzing factors such as sunlight angles, prevailing winds, and thermal inertia, architects can create spaces that are inherently comfortable and require far less energy to operate. Passive design not only delivers long-term cost savings but also ensures resilience as energy prices fluctuate and climate conditions become more extreme.
Advanced Insulation and Glazing
Investing in high-performance insulation and innovative glazing technologies is central to creating energy-efficient buildings. Superior insulation materials limit heat loss in winter and heat gain in summer, keeping interiors comfortable with minimal energy input. Meanwhile, advancements in window design—such as double and triple glazing, low-emissivity coatings, and dynamic shading systems—maximize natural light while reducing glare and unwanted heat transfer. The combined impact of these technologies results in lower utility bills and a significantly reduced carbon footprint.
Renewable Energy Integration
Modern green architecture often incorporates renewable energy systems to further reduce reliance on nonrenewable fuels. Photovoltaic panels, solar water heaters, and small-scale wind turbines are becoming common features on both residential and commercial buildings. By generating clean energy on site, these technologies help owners hedge against rising utility costs and support the broader transition to a low-carbon future. Moreover, integrating renewables into building design underscores a commitment to sustainability and positions properties as leaders in environmental innovation.
Healthy and Sustainable Living Environments
A key aspect of sustainable living environments is the promotion of superior indoor air quality. This is achieved through careful material selection—avoiding substances that off-gas harmful chemicals—and by incorporating effective ventilation systems. Use of non-toxic paints, adhesives, and finishes ensures that spaces remain free from pollutants and allergens. In addition, plants and biophilic design elements can further purify air and create a calming atmosphere. Improved indoor air quality has been shown to enhance cognitive function, reduce absenteeism, and support overall health, making it an essential pillar of green architecture.